Take a faster, smarter path to AI-driven C/C++ test automation. Discover how >>

Explore the Chapters
Safety-critical software development standards like ISO 26262 require that manufacturers prove that the tools they’re using to develop software provide correct and predictable results. The process of providing such evidence is known as tool qualification. While it’s a necessary process, tool qualification is often a tedious and time-consuming activity that many organizations fail to plan for.
The end deliverable is proof in the form of documentation, but there is more to the qualification process than just delivering a big pile of static documentation. Parasoft’s Qualification Kits for C/C++test, which include a convenient tool wizard that brings automation into the picture, reduce the time and effort required for tool qualification.
Tool qualification needs to start with tool selection, ensuring you are using a development tool that is certified by an organization, such as TÜV SÜD. This will significantly reduce the effort when it comes to tool qualification.
Parasoft C/C++test and C/C++test CT are certified by TÜV SÜD for functional safety according to IEC 61508, IEC 62304, EN 50128/EN 50716, and ISO 26262 standards for both host based and embedded target applications. The fully integrated testing solution for C/C++ software development paves the way for a streamlined qualification of static analysis, unit testing, and coverage requirements for the safety-critical standards.
Pre-certified tools are often enough for lower safety integrity levels such as ASIL A and B. However, for ASIL C and D, tool qualification requires further validation, usually requiring verification and validation of the tool itself on target system hardware.
Traditionally, tool qualification has meant significant amounts of manual labor, testing, and documenting to satisfy a certification audit. But this documentation-heavy process requires manual interpretation and completion. As a result, it’s time consuming and adds to an organization’s already heavy testing schedule and budget.
Parasoft leverages its own software test automation tool qualification with Qualification Kits, which include a documented workflow to dramatically reduce the amount of effort required.
There should be no need to do any extra work for qualifying capabilities not used during development. Reducing the scope of testing, reporting, and documentation is a key way to reduce the qualification workload.
The example below shows the use case of C/C++ static code analysis being used to check compliance to the MISRA C 2023 standard, as part of ISO 26262 qualification. The tool then selects only the parts of the qualification suite needed for this function.


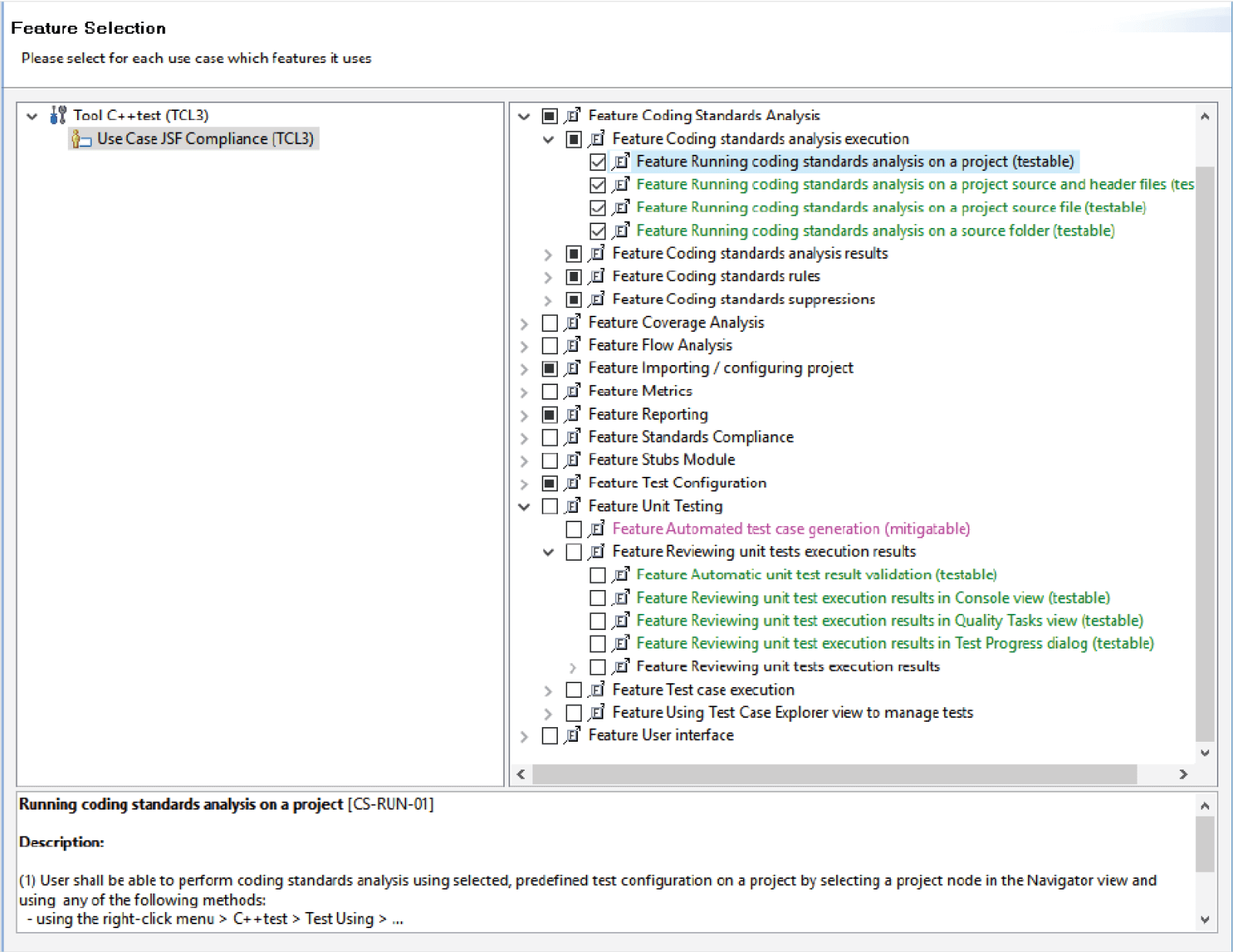
Parasoft Qualification Kits allow users to select the options required for their project. Upon selection, only tests and documentation are used and provided from this point forward.
A unique advantage to qualifying test automation tools is that the tools can be used to automate their own testing. Automating this as much as possible is key to making it as painless as possible. Even manual tests, which are inevitable for any development tool, are handled as efficiently as possible. Step by step instructions are provided and results are entered and stored as part of the qualification record.
Parasoft C/C++test and C/C++test CT collect and store all test results from each build, and tests run as they do for any type of project. These results are brought into the test status wizard in the Parasoft Qualification Kits to provide a comprehensive overview of the results like those shown below.
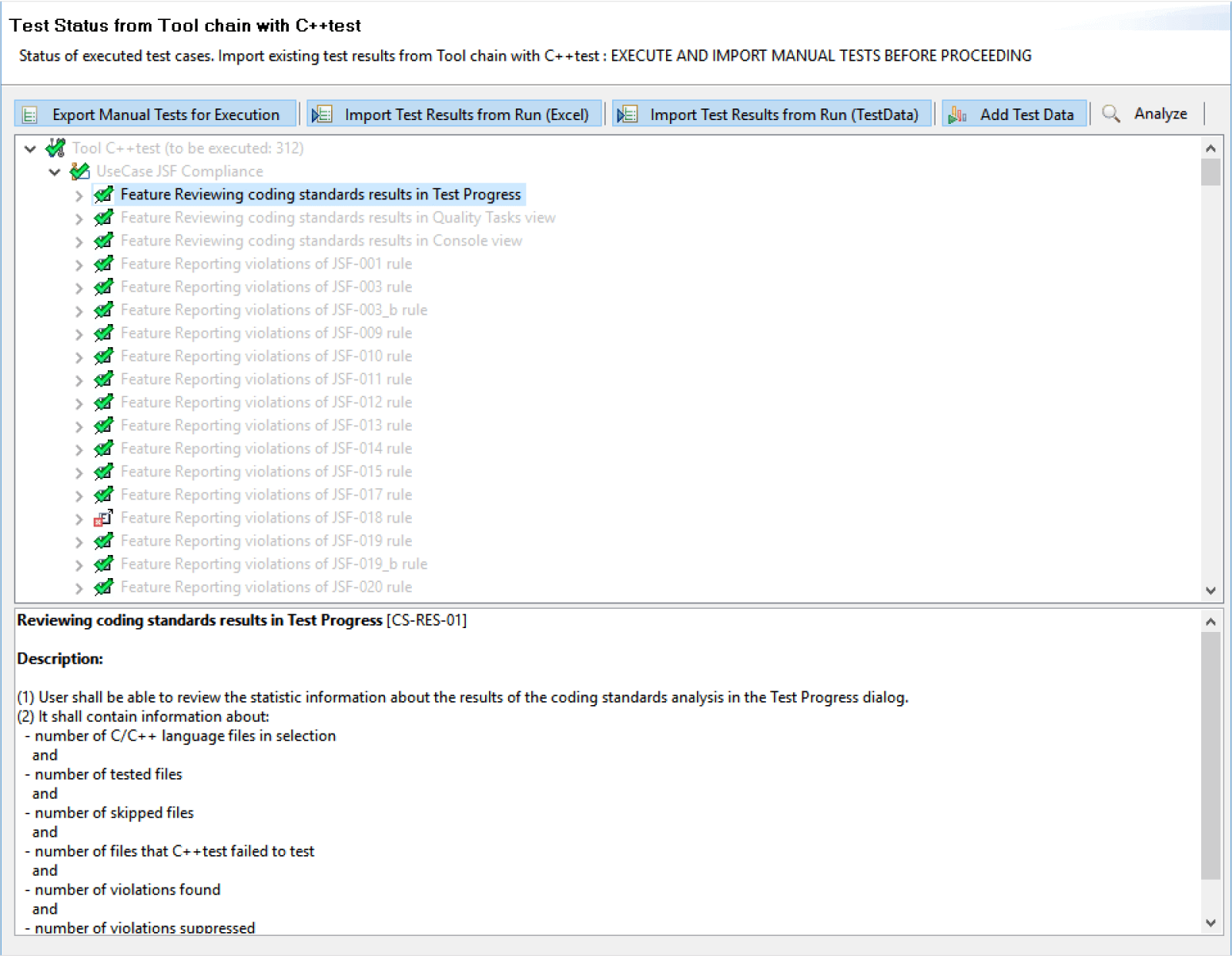
Leveraging centralized data collection and automating the qualification process greatly reduces manual tracking of compliance progress.
Every development tool has known bugs and any vendor selling products for safety-critical development must have these documented. There’s more to dealing with known defects than just documenting them. Tool qualification requires proof that these defects are not affecting the results used for verification and validation. For each known defect, the manufacturer must provide a mitigation for each one and document it to the satisfaction of the certifying auditor.
It’s incumbent on the tool vendor to automate the handling of known defects as much as possible. After all, the vendor is expecting customers to deal with third-party software bugs as part of their workload! The Parasoft C/C++test qualification kits include a wizard to automate the recording of mitigation for known defects as shown in the example below.
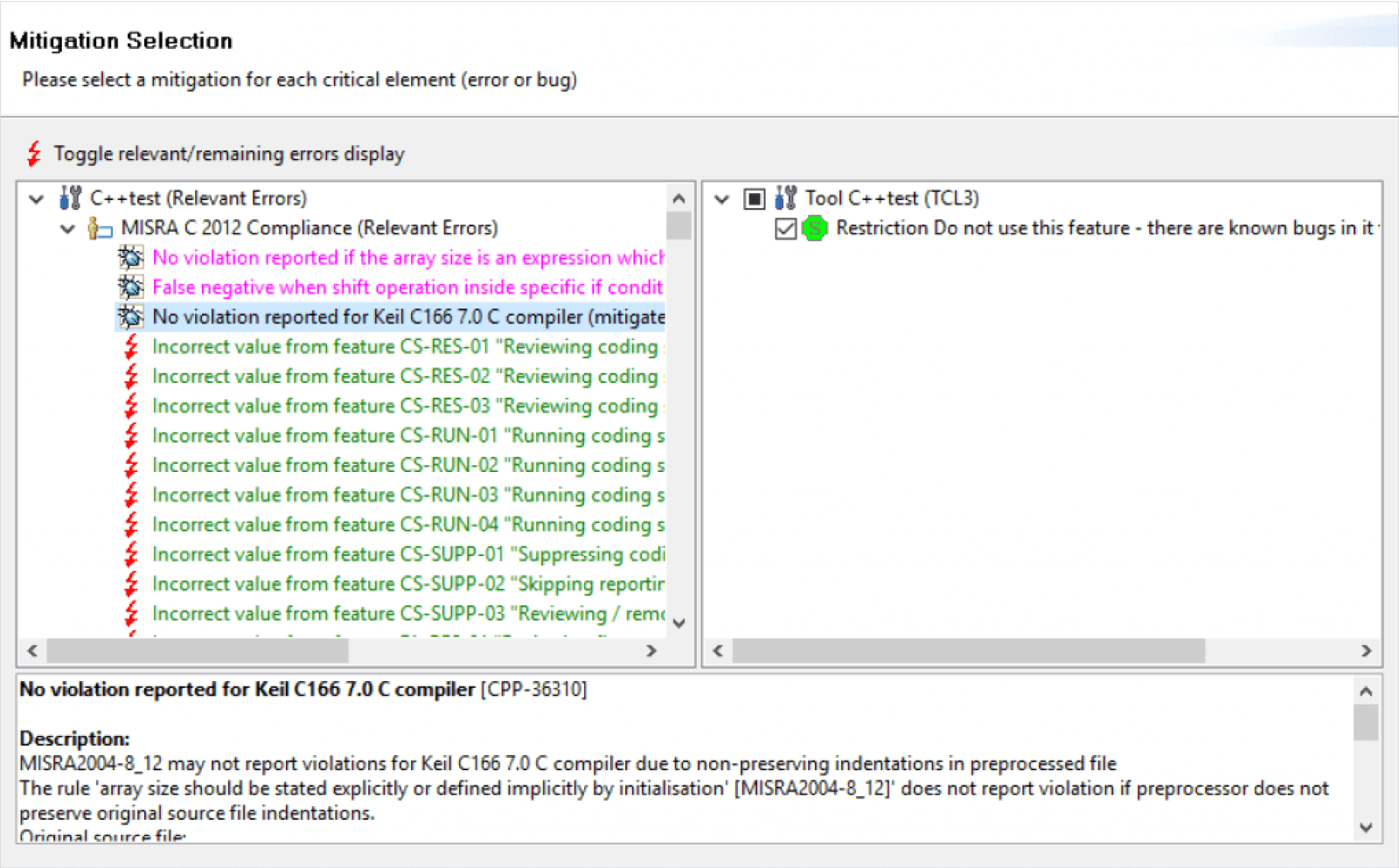
Known defects are managed directly in Parasoft C/C++test.
In each of these documents, only the documentation required for the tool features in use is generated because the scope of the qualification was narrowed down at the beginning of the project. Automation and narrowing the scope of qualification greatly reduces the documentation burden.

Explore the Chapters