Take a faster, smarter path to AI-driven C/C++ test automation. Discover how >>
Increase Unit Testing ROI With Automatic Unit Test Creation
Use the Parasoft Jtest automated unit test generation tool to boost your unit testing ROI. Read on to learn how to automate the tedious aspects of unit testing and reduce mocking complexity.

Use the Parasoft Jtest automated unit test generation tool to boost your unit testing ROI. Read on to learn how to automate the tedious aspects of unit testing and reduce mocking complexity.
Parasoft Jtest’s automatic unit test creation technology removes unit testing roadblocks, automating the mundane aspects of unit testing, including creation, isolation, mocking, and maintenance.
Most development teams will agree that, although they don’t like it, unit testing is, in fact, extremely valuable. Despite the many tools that help with manual test creation, creating and maintaining unit tests still requires a lot of manual, time-consuming, often mind-numbing effort before adding business logic to a test. As such, despite having the intention of great unit testing, development teams typically do the minimal amount of unit testing required or skip it altogether.
A recent customer survey revealed, somewhat expectedly, that test creation, mocking/isolation, and maintenance are key issues standing in the way of unit testing success. Figure 1 shows the results of this survey, showing the top concerns developers are identifying with unit testing in Java.
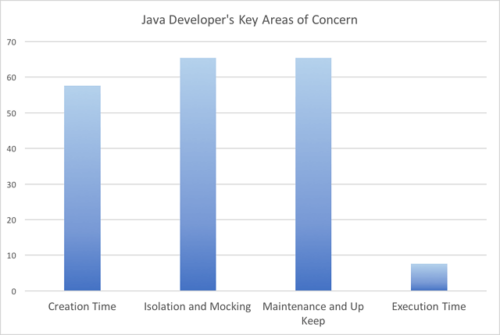
Survey results show key areas of concern as a percentage that arise from unit testing.
To address these main areas of concern, we can turn to automated software testing. In this blog, I’ll show you how to use Parasoft Jtest to automatically create unit tests, to save time and energy at test creation time. Parasoft Jtest’s automatic unit test creation technology sets up the test framework, instantiates objects, configures mocks for appropriate objects and method calls used by the method under test, and adds assertions. It creates regular JUnits, getting all the mundane work done so developers can focus on applying human intelligence and logic to their testing.
Every software engineer who understands the need to prioritize high-quality and bug-free code in software development will tell you that unit testing is like a bedrock upon which other aspects of software quality assurance are built. Unit testing ensures that individual units or components of code work as expected. It involves testing a small piece of code, typically a single function or method, in isolation from the rest of the system.
To ensure that each unit of code works as intended and performs the expected function assigned to it, developers write test cases either manually or with automatic unit test creation tools. Running these tests helps to identify any bugs or errors in the code before it’s integrated into the larger system. Running them regularly ensures that what works today continues to work in the future.
Unit testing has become increasingly important over the years, as software systems have become more complex and the need for reliable software has increased. However, to get the most value from unit tests, there are recommended policies and best practices that should guide the process.
For instance, Parasoft’s automated unit testing solution offers software developers AI-driven unit test generation that can be deployed to auto-generate robust and ready-to-run unit test cases quickly. It also provides IDE and CI/CD tools for running, extending, and maintaining those tests as code changes, and analysis of important metrics like code coverage.
While unit testing is crucial in every software development endeavor, it can also present several challenges that hinder its effectiveness. Below are some key challenges in unit testing and how to overcome them.
The challenge is that it can take a large amount of time and effort to achieve high levels of code coverage and unit testing often gets deprioritized in the face of schedules and pressure to develop new functionality. Using an automated tool like Parasoft Jtest can significantly reduce the amount of time it takes to create and maintain unit tests, making the creation of a sufficient number of unit tests achievable.
Furthermore, after committing code, the CI/CD process needs to execute unit tests to verify the changes. When there is a large suite of tests, they may not execute as quickly as desired. Parasoft Jtest identifies impacted tests that need to be run when code changes, in both the IDE and CI/CD process so that developers can identify and run an optimized set of changes that verify their changes.
Unit testing is iterative, and in Agile processes, unit testing has a good track record of improving project outcomes. It’s well-proven that testing earlier in the life cycle is the best way to detect and remove expensive and time-consuming system-level bugs. More specifically, the following are some key benefits of unit testing.
Unfortunately, regardless of these benefits, developers still struggle with unit testing, despite the desire to achieve better results. These struggles, also illustrated by the survey results above, include the following.
Software development teams must address these problems with test creation, isolation, and maintenance if they want to achieve the benefits of thorough unit testing, and the solution is automation. Parasoft Jtest’s automatic unit test creation tool provides the assistance teams need for test creation and maintenance while working within the developer’s IDE and leveraging existing test and mocking frameworks.
Creating unit tests is tedious and steers attention away from the more interesting parts of a project. The code itself is repetitive and often requires as much effort as the code under test. On top of that, the unit test code itself requires fixing and debugging, as any code would.
Fortunately, unit tests lend themselves well to automation. Automatic guidance from a unit testing tool has its advantages.
Many IDEs provide unit test creation wizards for JUnit, for example, but don’t provide "content" to complete the process. Assertions need to be manually defined, and if mocking frameworks are used, a significant amount of manual coding is required.
Instead, Parasoft Jtest provides real-time, context-aware assistance in the developer’s IDE. With automatic unit test creation, the content missing from simple skeleton unit tests is quickly and efficiently completed as you leverage your unit testing tool to perform the following:
To address this, let’s look at an example. Here, Parasoft Jtest’s Unit Test Assistant is used within an IDE to create a suite of tests:
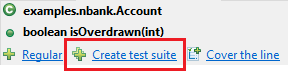
The tool creates multiple tests, each configured to cover a separate path through the method under test. For example, the generated code may look like this:
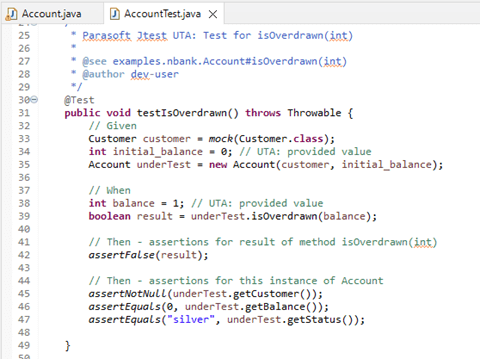
Note that the test is pre-configured with mocked objects and real values, as well as assertions on the result of the method under test and any objects that changed during execution (in this case, fields in the object under test changed).
Unit testing implies isolation of the object under test, which requires a fair amount of work if there are many dependencies. Even with mocking frameworks such as Mockito, there’s still significant manual coding required. With an automated test assistant tool, you can detect dependencies and automatically fill in the details required by the framework.
The tool itself analyzes the code under test, automatically detects dependencies, and makes recommendations to the developer.
For example, assume we execute a unit test containing the following code that mocks the class IWorkspaceClass:
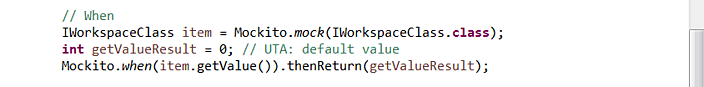
Dependencies are detected during runtime and the tool recommends mocking the dependencies that it has found:
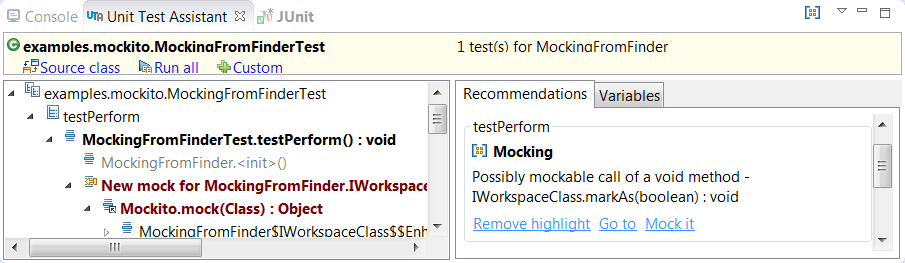
Selecting "Mock It" with the tool generates the necessary mocking code with the unit test. Once this code is generated, it can be customized to represent the logic required by the test. Automated detection of dependencies and subsequent mocking code creation greatly reduces the amount of manual, and potentially error-prone, coding required to mock objects.
Maintenance of test suites overlaps much of the work required for test creation, such as creating new tests, modifying tests to properly cover the underlying logic, mocking dependencies, and executing tests. Getting assistance from Parasoft Jtest’s Unit Test Assistant during test maintenance is just as valuable as during creation, as it provides runtime analysis results collected during test execution. For example, a new dependency in an object under test is detected at runtime and the tool prompts the developer on how to deal with it.
Equally critical during this phase is ensuring that the assertions are still valid. The Parasoft Jtest Unit Test Assistant provides recommendations that can detect changes in the code and update assertions to reflect new business logic.
Java developers already unit testing are likely using JUnit and possibly a mocking framework for their project, such as Mockito. Test automation tools need to leverage these existing tools, since replacing an existing investment in unit testing would eliminate any cost and time benefit to be had by using an automated tool. Parasoft Jtest’s Unit Test Assistant integrates seamlessly with these existing tools, which is critical.
Unit testing has clear benefits. Although most development teams realize this, many are stymied by the effort of creating and maintaining tests. Using automated unit testing technologies like those in Parasoft Jtest will help users knock down these roadblocks, automating the mundane aspects of unit testing, including creation, isolation, mocking, and maintenance. To accelerate adoption, Parasoft Jtest leverages the development team’s existing investment in test and mocking frameworks and gives back time to the developer while bringing quality back to the product.