See what API testing solution came out on top in the GigaOm Radar Report. Get your free analyst report >>


See what API testing solution came out on top in the GigaOm Radar Report. Get your free analyst report >>
Jump to Section
There's no denying the importance of integrating CI/CD for quality assurance purposes in software development. Here's a discussion on how to use automation tools to implement QA in a CI/CD pipeline.
Jump to Section
Jump to Section
The CI/CD pipeline has been adopted by many companies to streamline their software development in the last few years. After all, modern workflows exist to make everyone’s lives easier and companies more efficient. When testing in DevOps environments, both productivity and accuracy are vital. That’s why deployment automation features so heavily across many software development modalities.
However, as with anything that includes test builds and revisions, CI/CD pipelines require the implementation of robust QA testing practices. These automated testing methods improve existing manual testing processes by reducing the amount of time and work required. Detecting issues early and ensuring you have a bug fix in place will only streamline the process further.
But what are the “meat and potatoes” of continuous integration and continuous delivery (or deployment) pipelines? Are there specific CI/CD tools every company needs or just focused ones tailored to meet certain use cases?

A CI/CD pipeline simply automates how software is delivered. In the pipeline, code is built and tests are run via continuous integration. Then, the automated process deploys the updated version of the code.
Continuous integration combines work across multiple developers into a common mainline throughout a workday or cycle. This helps to avoid integration conflicts as the update branches never develop too far from the mainline codebase.
Automated testing usually occurs at this point in the workflow. This ensures enhanced economical performance and improves early bug detection.
The continuous delivery approach requires that development teams edit code in shorter cycles. Not only can the code then be updated at any point, but it allows for a more streamlined build, test, and release workflow. This also reduces overall costs and risks associated with any development projects.
From bug fixes to feature updates, continuous delivery makes releasing changes for the production-end stage of development much less of an inconvenience.
These two aspects of the pipeline both occur after continuous integration which has a greater focus on testing. Continuous delivery, in contrast, automatically pushes code changes to a development environment. This pairs automated testing with automated release for greater ease of analysis, bug fixes, and updating.
Continuous deployment is a similar process as continuous delivery but operates with the production environment instead of a test environment. This stage in the pipeline relies on automated deployments without the need of human intervention. Any approved changes to the code get pushed to production right away.
Both processes deliver something everyone needs when it comes to scheduled maintenance: predictability.
The process by which both continuous integration and continuous delivery happen is a multi-step workflow with a few elements involved. As mentioned, it involves updating the mainline several times a day with various updates across multiple developers or teams.
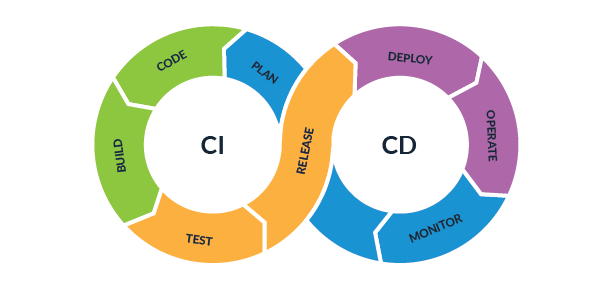
But the simplest breakdown involves five major categories: build, test, release, deploy, and validate. While these tasks can be addressed using specific tools, they can also be addressed by automated tool suites or one service alone.
Each of the five CI/CD pipeline categories has its own sub-tasks.
Of course, these processes will vary from team to team and company to company.
DevOps and software development teams with multiple silos or units will benefit most from CI/CD pipelines. The workflow will help bridge the version differences and eliminate the need for inefficient briefings on changes. The automated processes also help to remove errors, produce quick iterations, and even give developers standardized feedback loops.
Whether your company works on hospital databases, software as a service (SaaS) products, or on safety-critical applications, CI/CD pipelines can improve your workflow efficiency and product accuracy. But it requires the right QA processes to be the most effective.
Furthermore, anyone in IT leadership positions needs to fully grasp CI/CD pipeline implementation. It enables your businesses to keep pace with your competitors which, as industry members know, is a never-ending challenge.
Azure DevOps Project is a great tool for simplifying how teams set up a CI/CD pipeline using Azure DevOps. Use your own code or one from a sample application to deploy applications across services such as the SQL database, virtual machines, and more.
The pipeline will help commit any changes to GitHub then deploy them automatically to Azure. This kind of reliable automation is just one feature of an effective CI/CD pipeline.
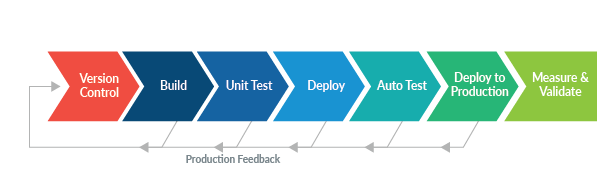
The biggest aspect of the CI/CD pipeline workflow is the feedback loop it provides to make the “continuous” part work properly. Any hang-ups in the loop cause inefficiencies which then lead to delays in development and deployment.
But the essential workflow hinges upon the automated testing aspect. Version control merges all changes to the main repository. After deployment to the test environment, automated testing begins. In the final stage of continuous deployment, this is the last moment when production feedback can take place.
After that, validation and measuring can begin.
A good CI/CD pipeline needs four things to provide significant benefits to the organization:
The overall strategy here is to “do more with less” while also increasing output accuracy and efficiency. Automation plays a key role in facilitating the other three facets of great continuous integration and continuous delivery pipelines.
Apart from the obvious benefits of reliability, automation, and enhanced speed, CI/CD pipelines provide many other additional benefits. Teams can leverage their improved release cycles to refine their bug fix workflows. They can utilize the upgraded code quality to collaborate across new initiatives or to reassess current projects.
In short, CI/CD pipelines provide:
The list really does go on! Implementing QA in CI/CD pipelines is the final step in creating a system that truly outputs the maximum amount of benefits in the minimum amount of time for your DevOps teams.
There are many CI and CD tools available on the market, but not all of them will be needed for every company or team. Parasoft partners with the leading providers to ensure CI/CD integrations across tools such as:
There’s plenty to learn about our catalog of tool integrations that continues to grow with GitHub being the most recent addition.
These automated pipelines deliver increased reliability, speed, communication, and more for software teams. But, despite the many benefits of continuous integration and continuous delivery, every system is not without its pitfalls.
Think of your CI/CD pipeline like a carbon fiber bike frame. It’s lighter, lets you go faster, and just enhances performance overall. But when it hits its breaking point, it requires immediate attention. Unlike carbon fiber, however, CI/CD pipelines don’t require total replacement when teams encounter issues.
They just need to remember a few important things to maintain the health of their systems.
One of the most common issues with CI/CD pipelines involves UI testing with Selenium. CI/CD can exacerbate Selenium test woes such as false negatives on regressions and defects.
Parasoft sought to tackle this issue directly with Parasoft Selenic—a tool that automates the analysis and correction of test issues specific to Selenium. The tool merely shifts the workload onto the CI system, so that the human developers don’t need to root out the problems (if there are any real issues at all).
Other common problems include:
Though not an exhaustive list, these are the most common CI/CD pipeline issues. As is the nature of software development, however, one team may encounter unique issues that require innovative solutions.
Manual testing is, by no means, an unnecessary approach, but automated testing, without question, must have a place in your CI/CD pipeline. Teams that want to improve their agility will need to be more flexible and the first step is test automation.
It must also be said that automating a CI/CD pipeline and integrating test automation are two different things. After all, testing is simply one part of the pipeline process. Automating the whole pipeline is a different task entirely.
Software engineers will be very familiar with functional test automation. Utilizing it allows developers to move forward with new elements or features quickly. Features like Parasoft’s Smart Test Execution ensure that each category is covered with faster results access, optimized automated tests, continuous testing, and more.
But automation is not limited to functional testing alone. Performance testing is now an integral part of continuous application delivery. Adding specific performance tests to tools such as Jenkins is just one way that teams can improve their CI/CD pipelines. These tests will naturally operate on a regular basis to provide better and earlier bug detection, as well as assess build compatibilities.
The collection of analysis of performance test results can be automated, as well, for further agility. Parasoft Load Test provides key insights to keep augmenting your processes.

Integrating automated testing into a system is a crucial part of any pipeline workflow.
But shortening a feedback loop is one of the not-so-secret tips to creating an effective CI/CD pipeline. The shorter the time that developers spend waiting on test results, the more time they’ll have to address bug fixes and make code changes.
Automated testing allows for scalability—an unskippable part of software development for companies looking to expand or grow. In fact, there really is no reason not to implement automated testing with a CI/CD pipeline.
The role of automated testing in CI/CD pipelines is as flexible as the pipelines themselves. Moreover, manual testing is not nearly as agile as automated testing can be. Teams can more easily tackle a wider array of tests using CI/CD automation.
For example, companies can address the following types of tests:
Many tests can and should also be run in parallel in order to increase efficiency. From version control to regression testing and even service virtualization, continuous integration and continuous delivery systems are the best way to make your development teams better.
Developers focused on UI elements and behavior can also leverage cross-browser testing which is exactly what it sounds like: testing a website across various browsers to identify UI anomalies. Tools such as Parasoft Selenic—an AI and machine learning-powered UI testing tool—aim to improve this aspect of automated testing.
However, it’s important to go beyond UI testing to reach your software quality goals. Smart test generation uses AI to leverage UI tests for automatically creating other functional and nonfunctional tests. Our Parasoft Jtest and SOAtest tools also augment existing unit test and API test best practices.
Reliable QA pipelines hinge upon the automated systems behind them. These allow for stable integration and delivery on a regular basis. But simplifying these aspects is pivotal in extracting as much value out of your CI/CD pipeline as possible.
Implementing a CI/CD pipeline with QA doesn’t need to be a drawn-out headache. In fact, it can be whittled down to a few key aspects alone:
Pipelines work for small projects, mid-size firms, and at scale. All it takes is a pragmatic approach to the implementation to achieve improved performance, efficiency, ROIs, and reduced cost.
At Parasoft, we live by the phrase “Test Early – Test Continuously.” Paired with automated compliance and leveraging AI, our tools aim to make lives for human developers and testers just a bit easier. Implementing a CI/CD pipeline with QA is just another way to accomplish this goal.